Summary:
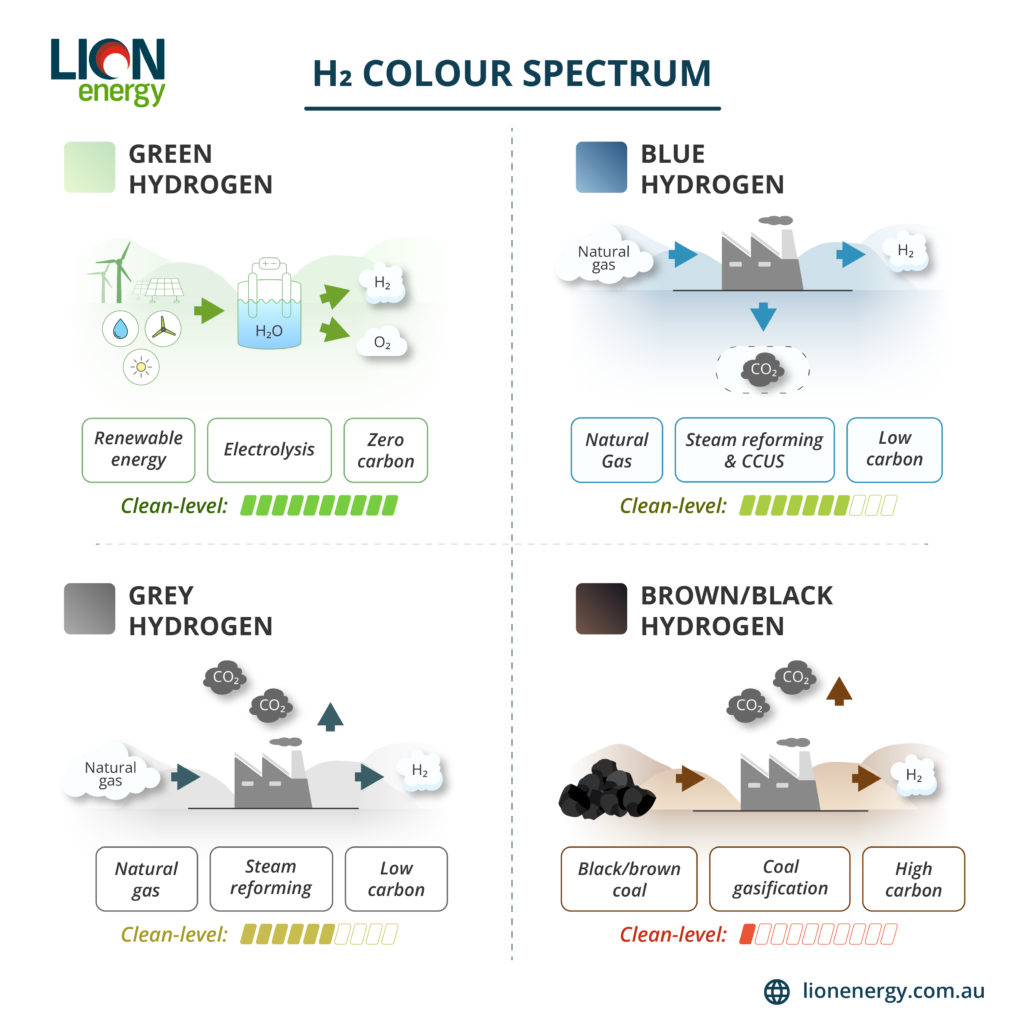
Hydrogen is classified by color to indicate its production method and environmental impact. Green hydrogen, produced using renewable energy, is the cleanest and most sustainable option. Blue hydrogen has lower emissions due to carbon capture, while grey hydrogen, derived from natural gas, still contributes to pollution. The most harmful is brown/black hydrogen, produced from coal. As the world shifts toward cleaner energy, green hydrogen emerges as the key to a sustainable future.
Green Hydrogen: The Cleanest Choice
Produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like wind and solar, green hydrogen generates no carbon emissions. It is the most environmentally friendly option and plays a crucial role in reducing global dependence on fossil fuels. Lion Energy is committed to advancing green hydrogen production to support a sustainable future.
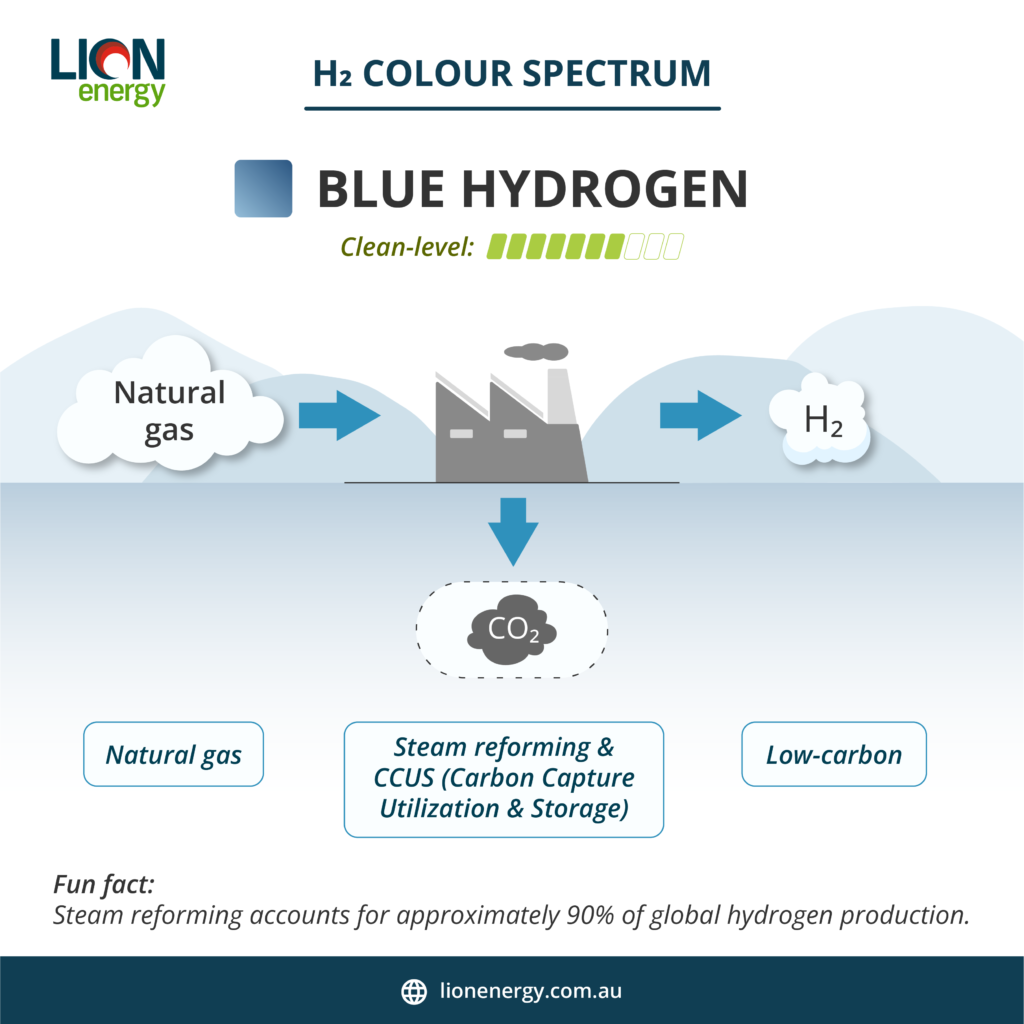
Blue Hydrogen: A Lower-Carbon Alternative
Blue hydrogen is derived from natural gas, but unlike grey hydrogen, its carbon emissions are partially mitigated through carbon capture and storage (CCS). While it is not completely carbon-free, it offers a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based hydrogen production.
Grey Hydrogen: A High-Emission Process
Grey hydrogen is also produced from natural gas but without carbon capture measures. This process releases large amounts of CO₂ into the atmosphere, making it a significant contributor to climate change and air pollution.
Brown/Black Hydrogen: The Most Polluting
Derived from coal gasification, brown and black hydrogen have the highest carbon footprint. Their production process releases vast amounts of greenhouse gases, exacerbating global warming and environmental degradation.
A Future Powered by Green Hydrogen
With industries aiming for net-zero emissions, green hydrogen is emerging as the key to decarbonization. Prioritizing clean hydrogen solutions helps pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy future.